In today’s interconnected technological landscape, micro connectors serve as the invisible heroes enabling seamless communication between devices, systems, and platforms across industries worldwide.
🔌 The Rising Importance of Micro Connectivity
The digital transformation has accelerated the demand for smaller, more efficient connection solutions. Micro connectors have evolved from simple physical interfaces to sophisticated components that facilitate data transfer, power delivery, and signal transmission in increasingly compact form factors. These miniature marvels are now fundamental to everything from consumer electronics to aerospace applications, making their reliability and trustworthiness non-negotiable.
As devices shrink and functionality expands, engineers face the challenge of maintaining robust connectivity while reducing physical footprints. The market for micro connectors has grown exponentially, with projections indicating continued expansion as IoT devices, wearable technology, and medical implants become ubiquitous. This growth underscores the critical need for crafting connectors that not only fit within tight spatial constraints but also deliver consistent performance under varying environmental conditions.
Understanding the Anatomy of Trustworthy Micro Connectors
A trustworthy micro connector is defined by several critical characteristics that distinguish premium solutions from basic alternatives. Material selection forms the foundation of connector reliability, with considerations spanning electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. High-quality connectors typically employ gold-plated contacts for superior conductivity and oxidation resistance, while housing materials range from engineered thermoplastics to metal alloys depending on application requirements.
The contact design itself represents a sophisticated engineering challenge. Designers must optimize contact force to ensure reliable electrical connection without causing excessive wear or requiring prohibitive mating forces. Spring geometries, contact shapes, and surface treatments all play crucial roles in achieving this balance. Modern micro connectors often incorporate multiple contact points per connection to provide redundancy and enhance reliability.
Critical Design Parameters for Integration Success
Successful integration of micro connectors demands attention to numerous design parameters that impact both immediate functionality and long-term performance. Pitch spacing—the distance between adjacent contacts—directly influences connector density and miniaturization potential. Modern applications frequently require pitches of 0.5mm or less, presenting significant manufacturing and assembly challenges.
Insertion and extraction forces must be carefully calibrated. Too much force risks damaging delicate components or making manual assembly impractical, while insufficient force may result in intermittent connections or accidental disconnections. Retention mechanisms ranging from simple friction fits to sophisticated locking systems provide mechanical security appropriate to application vibration profiles and handling requirements.
Environmental sealing represents another crucial consideration. Applications in medical, automotive, and industrial environments often expose connectors to moisture, dust, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. Appropriate sealing solutions—from simple gasketing to hermetic sealing—protect electrical interfaces while maintaining compact dimensions.
⚙️ Manufacturing Excellence: Where Precision Meets Scalability
The manufacturing of micro connectors demands exceptional precision and process control. Modern production facilities employ advanced stamping and forming technologies capable of achieving tolerances measured in microns. Progressive die stamping enables high-volume production of complex contact geometries while maintaining dimensional consistency critical for reliable electrical performance.
Plating processes require equally rigorous control. Selective gold plating concentrates precious metals on mating surfaces while reducing material costs. Nickel underplating provides a diffusion barrier preventing gold migration into base materials, which could compromise conductivity over time. Automated optical inspection systems verify plating thickness and coverage, catching defects before they reach assembly stages.
Insert molding technology has revolutionized connector housing production, enabling complex geometries with integrated mounting features, alignment guides, and sealing surfaces. This process overmolds thermoplastic materials around pre-positioned contact arrays, creating monolithic structures that enhance mechanical strength while reducing assembly complexity. The precision required demands sophisticated tooling and process monitoring to prevent flash, short shots, and dimensional variations.
Quality Assurance Throughout the Production Chain
Quality assurance for micro connectors extends beyond final inspection to encompass in-process verification at every manufacturing stage. Statistical process control monitors critical dimensions and characteristics, enabling early detection of process drift before defective products are produced. Automated testing systems verify electrical continuity, contact resistance, and insulation resistance on 100% of production units for high-reliability applications.
Environmental stress screening subjects connectors to accelerated aging conditions—temperature cycling, humidity exposure, vibration, and mechanical cycling—revealing latent defects and validating design margins. These tests simulate years of field use in compressed timeframes, providing confidence in long-term reliability predictions.
🎯 Application-Specific Optimization Strategies
Different applications present unique challenges requiring tailored connector solutions. Consumer electronics prioritize cost efficiency, compact dimensions, and ease of automated assembly. High-volume production demands connector designs that accommodate pick-and-place equipment tolerances while maintaining reliable electrical performance despite minimal contact force and basic environmental protection.
Medical devices impose stringent biocompatibility requirements alongside reliability expectations that often exceed consumer electronics by orders of magnitude. Connectors for implantable devices must function flawlessly for years within corrosive body fluid environments while maintaining hermetic sealing to protect internal electronics. Material selections exclude substances that might provoke immune responses, and sterilization compatibility becomes mandatory.
Aerospace and defense applications demand connectors capable of withstanding extreme temperatures, shock, vibration, and electromagnetic interference while maintaining signal integrity for high-frequency communications. Weight optimization takes priority, driving extensive use of advanced materials and hollow contact designs that reduce mass without compromising electrical or mechanical performance.
Signal Integrity Considerations for High-Speed Data
As data rates increase, signal integrity becomes paramount. High-speed micro connectors must minimize impedance discontinuities, crosstalk, and electromagnetic interference that degrade signal quality. Controlled impedance designs maintain consistent electrical characteristics throughout the signal path, typically achieved through precise control of contact geometry and dielectric material properties.
Differential pair routing within connectors preserves the balanced signaling essential for modern serial communication protocols. Shielding strategies—from individual contact shielding to overall connector shells—contain electromagnetic emissions and reject external interference. Ground contact placement provides return current paths that minimize loop areas and associated inductance.
🔬 Testing Protocols That Build Confidence
Comprehensive testing validates connector performance across expected operating conditions and failure modes. Mechanical testing encompasses mating cycle endurance, retention force verification, and vibration resistance. High-reliability connectors may require durability through thousands or even millions of mating cycles, with contact resistance monitored throughout to detect degradation trends.
Electrical testing verifies parameters including contact resistance, insulation resistance, dielectric withstanding voltage, and current-carrying capacity. High-speed connectors undergo additional characterization using vector network analyzers to measure insertion loss, return loss, and crosstalk across relevant frequency ranges. These measurements validate impedance control and signal integrity performance.
Environmental testing subjects connectors to temperature extremes, thermal cycling, humidity, salt spray, and chemical exposure representative of application environments. These tests reveal material compatibility issues, seal effectiveness, and potential degradation mechanisms before field deployment. Accelerated life testing extrapolates long-term reliability from compressed exposure profiles.
⚡ Power Delivery in Miniature Packages
Modern micro connectors increasingly handle significant power alongside data signals. This dual functionality presents thermal management challenges as current flow generates resistive heating in compact contact structures. Connector designers must balance contact size reduction against current-carrying requirements, employing advanced materials and geometries to maximize conductivity while minimizing volume.
Contact resistance directly impacts power efficiency and thermal generation. Gold plating reduces resistance while preventing oxidation that would increase resistance over time. Contact force optimization ensures stable, low-resistance interfaces throughout operational life despite vibration, thermal cycling, and other stresses that might otherwise compromise electrical performance.
Thermal modeling predicts temperature distributions within connectors and adjacent components, guiding design modifications that enhance heat dissipation. Increased contact cross-sections, thermally conductive housing materials, and strategic ventilation improve thermal performance. Some designs incorporate dedicated thermal management features such as heat sinks or thermal vias that conduct heat away from contact interfaces.
🌍 Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
Environmental consciousness increasingly influences connector design and manufacturing. Regulatory compliance with directives such as RoHS and REACH restricts hazardous substances, driving adoption of alternative materials and processes. Lead-free plating and soldering technologies have become standard, though implementation required extensive qualification to ensure reliability matching traditional approaches.
Material recyclability considerations guide selection decisions, favoring polymers and metals with established recycling streams. Design for disassembly facilitates end-of-life component recovery and material sorting. Some manufacturers implement take-back programs that recover and recycle connectors from retired equipment, closing material loops and reducing environmental impact.
Manufacturing process optimization reduces waste and energy consumption. Precision manufacturing techniques minimize scrap generation, while efficient plating processes reduce precious metal usage and chemical waste. Lean manufacturing principles streamline production flows, reducing inventory requirements and associated resource consumption.
🚀 Future Trends Shaping Micro Connector Evolution
Emerging technologies drive continued micro connector innovation. The proliferation of 5G communications demands connectors supporting millimeter-wave frequencies with minimal signal degradation. These extreme frequency requirements necessitate unprecedented precision in impedance control and electromagnetic shielding, pushing manufacturing capabilities to new limits.
Flexible and stretchable electronics enable new form factors for wearable devices and conformable sensors. Connectors for these applications must accommodate mechanical flexing and stretching while maintaining electrical continuity—requirements that challenge traditional rigid contact designs. New approaches incorporating stretchable conductors and flexible substrates are emerging to address these demands.
Optical interconnects offer bandwidth and electromagnetic immunity advantages over electrical connections. Micro optical connectors bring fiber-optic technology to compact devices, enabling data rates far exceeding electrical alternatives. Alignment precision requirements intensify for optical interfaces, demanding innovative coupling mechanisms and self-alignment features.
Smart Connectors with Embedded Intelligence
Integration of active electronics within connector assemblies creates “smart connectors” with enhanced functionality. Embedded chips can provide authentication, configuration data storage, power management, or signal conditioning. These intelligent interfaces simplify system design while enabling new capabilities such as plug-and-play configuration and usage monitoring.
Authentication features combat counterfeit components by verifying connector genuineness before enabling system operation. Configuration data stored in connector memory automatically configures host systems for optimal performance with connected peripherals. Power management circuits protect against overcurrent conditions and optimize charging profiles for battery-powered devices.
💡 Best Practices for Seamless Integration
Successful micro connector integration begins with early supplier engagement during product development. Connector manufacturers possess specialized expertise that can guide design decisions, preventing costly changes during later development stages. Collaborative design reviews identify potential issues with accessibility, routing, mechanical stress, and manufacturing compatibility before commitments to tooling and production.
Proper PCB layout considers connector footprint requirements, including keepout zones for housing features and mating components. Signal routing from connector contacts must maintain impedance control and minimize crosstalk for high-speed applications. Ground plane continuity and appropriate via placement support electromagnetic shielding effectiveness.
Assembly process development ensures reliable connector placement and soldering. Automated assembly equipment requires consideration of connector orientation features, vacuum pickup surfaces, and vision alignment targets. Reflow soldering profiles must accommodate connector thermal limitations while achieving reliable solder joints. Post-assembly inspection verifies correct placement, soldering quality, and absence of contamination.
🔧 Troubleshooting Common Integration Challenges
Intermittent connections often result from inadequate contact force, contamination, or mechanical stress. Verification of proper connector seating and locking mechanism engagement resolves many such issues. Contact cleaning removes oxidation or contamination that increases resistance or causes opens. Mechanical stress relief prevents cable movement from translating to connector contacts, which might otherwise cause wear or fatigue failures.
Signal integrity problems in high-speed applications typically trace to impedance discontinuities or inadequate shielding. Verification of PCB layout compliance with design guidelines often reveals routing errors or missing ground connections. Connector orientation and positioning relative to metal enclosures affects shielding effectiveness and may require adjustment to minimize electromagnetic coupling.
Thermal issues manifest as elevated temperatures at connector interfaces or adjacent components. Contact resistance measurement identifies high-resistance connections requiring rework or replacement. Current distribution analysis may reveal imbalanced loading that concentrates current through limited contacts. Design modifications incorporating additional power contacts or enhanced thermal management resolve persistent thermal problems.
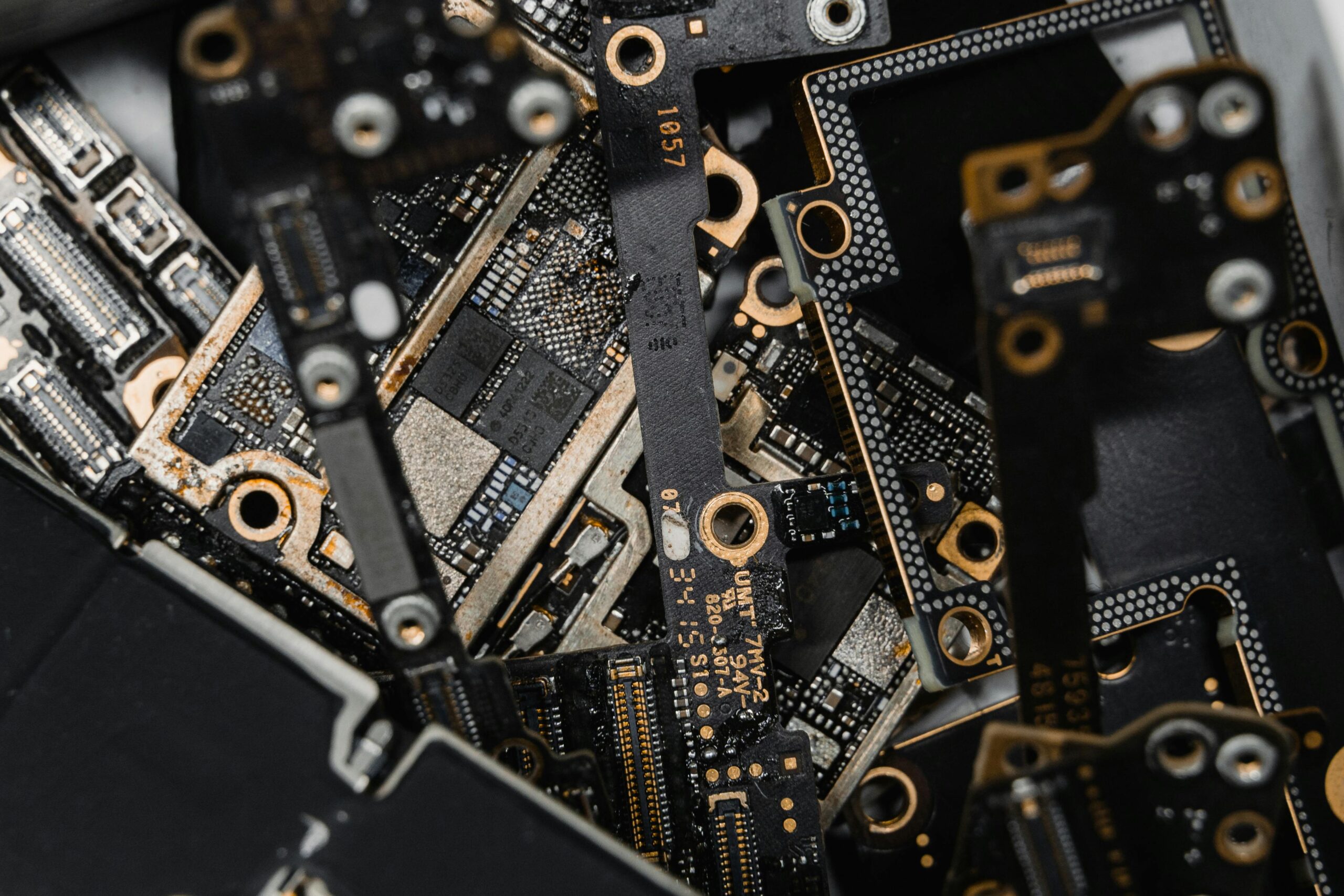
Building Long-Term Supplier Partnerships
Selecting the right connector supplier extends beyond component specifications to encompass technical support, quality systems, and long-term viability. Suppliers with robust quality management systems, comprehensive testing capabilities, and proven track records minimize risks associated with connector performance failures. Technical support teams that understand application requirements and provide responsive engineering assistance add significant value throughout product lifecycles.
Supply chain stability becomes increasingly critical as product lifecycles extend and volume requirements fluctuate. Suppliers with multiple manufacturing locations, diversified material sourcing, and inventory management programs mitigate supply disruption risks. Long-term availability commitments prevent obsolescence issues that could require costly product redesigns.
The journey toward crafting trustworthy micro connectors for seamless integration demands multidisciplinary expertise spanning materials science, mechanical engineering, electrical design, and manufacturing technology. Organizations that master these disciplines while maintaining focus on quality, reliability, and customer collaboration position themselves as leaders in enabling the connected devices that define modern technology. As miniaturization continues and performance requirements intensify, these mini marvels will remain essential enablers of innovation across industries worldwide.
Toni Santos is a microfluidic systems researcher and thermal micro-engineer specializing in the study of cell-flow control architectures, miniaturized fluid dynamics, and integrated micro-sensor platforms. Through an interdisciplinary and precision-focused lens, Toni investigates how biological and synthetic systems regulate flow, heat, and sensing at the microscale — across lab-on-chip devices, biomedical instruments, and thermal management systems. His work is grounded in a fascination with fluids not only as transport media, but as carriers of thermal and cellular information. From microfluidic control strategies to thermal gradients and embedded sensor networks, Toni uncovers the engineering and analytical tools through which systems achieve precision at diminishing scales. With a background in fluid mechanics and micro-device fabrication, Toni blends computational modeling with experimental validation to reveal how miniaturized systems regulate flow, temperature, and real-time detection. As the creative mind behind trovanyx, Toni curates technical insights, experimental case studies, and engineering interpretations that advance the integration of flow control, sensor technology, and thermal regulation at the microscale. His work is a tribute to: The precise manipulation of Cell-Flow Control in Microchannels The engineered scaling of Fluid Dynamics Miniaturization Techniques The responsive embedding of Micro-Sensor Integration Arrays The adaptive management of Thermal Micro-Regulation and Heat Flow Whether you're a microfluidics engineer, thermal systems designer, or curious explorer of microscale innovation, Toni invites you to explore the hidden mechanics of flow and heat — one channel, one sensor, one gradient at a time.




